What is a product designer? If you wish to know, you’ve come to the right place. This post will look at what a product designer does in user experience and discuss some of the most critical responsibilities and skills needed to succeed in this field. So whether you’re just starting your UX journey or looking to hire a product designer for your team, read on!
What is a product designer?
Product designers are significant to the process of making any app, website, or piece of software. These professionals know a lot about user experience (UX) design, and they work hard to make elements that are interesting and easy to use and meet users’ needs.
Product designers often start by gathering information about users through focus groups, interviews, and surveys. Then, they use this information to set goals and objectives for the product before they start wireframing and making prototypes.
From there, UX designers use detailed sketches and examples to build a fully developed prototype with the critical parts needed for a successful product design.
Product designers leverage innovative technology and user feedback to create attractive, highly functional products. They also know how to use new technology and user feedback to make products look good and work well.
In short, they work on all parts of UX design, from analysis to implementation, to ensure that the finished product meets users’ needs.
What is a UX-rich product?
At its core, a UX product is about improving the user’s experience. Not just that, but a broad spectrum of industries can benefit from a UX-rich product. It can be used to improve customer service interactions and develop new marketing strategies. Any business or organization can benefit from creating a UX product.
What is a Product Design System?
A product designer’s job is to ensure that the product design system is followed and is easy to understand. It is a library of reusable components, patterns, and rules that allow designers and developers to build products consistently and cohesively.
A sound design system will include everything from straightforward typography and colors to more complex interface components and animations. A sound design system will include everything from straightforward typography and colors to more complex interface components and animations.
By using a design system, teams can avoid reinventing the wheel with each new project and ensure that their products look and feel unified.
Product designers vs. UX designers: What’s the difference?
Product designers pay attention to every detail of the product, ensuring the final result is perfect for the client’s organization. They assist UX designers and are required to have a solid grasp of UX fundamentals.
Conversely, user experience designers (UX designers) focus on certain aspects of the design process to guarantee the most outstanding product for the user. They often invest more heavily in the initial design stage of the product.
Types of Product Design
System design
System design is about the big-picture of the product. It encompasses how all the components work optimally and how the user will interact with the product.
Process design
Process design is about ensuring the user’s experience is smooth and efficient. It focuses on optimizing the flow of tasks and creating a logical sequence for users to follow.
Interface design
It all comes down to making things simple to find, try, and use. It involves creating an appealing visual style and crafting clear and concise labels, buttons, and menus.
Roles and Responsibilities of the Product Designer

The roles of a product designer include, but are not limited to:
- Product designers are involved in the early stages of user experience design, working with team members to create prototypes and wireframes.
- A product designer must have high practical knowledge of the UX principles and be able to use them effectively in their design. They might also have to spearhead A/B testing and other UX research processes and methodologies to improve the user experience.
- They must have strong analytical skills and be able to interpret customer feedback quickly and accurately.
- Lastly, they collaborate with other departments, such as development and marketing, to ensure that all aspects of the product work together.
- Product designers ensure that every part of a product gives the user a great experience. They work on everything from the overall system design to the tiniest user interface details. They focus on making sure the product is easy and enjoyable to use.
Responsibilities of the Product Designer:
- Identifying new product development opportunities
- Examining the compatibility of a new product with market needs and consumer preferences.
- Establishing design specifications based on briefs from internal teams and external partners.
Product Designer’s Artifacts:
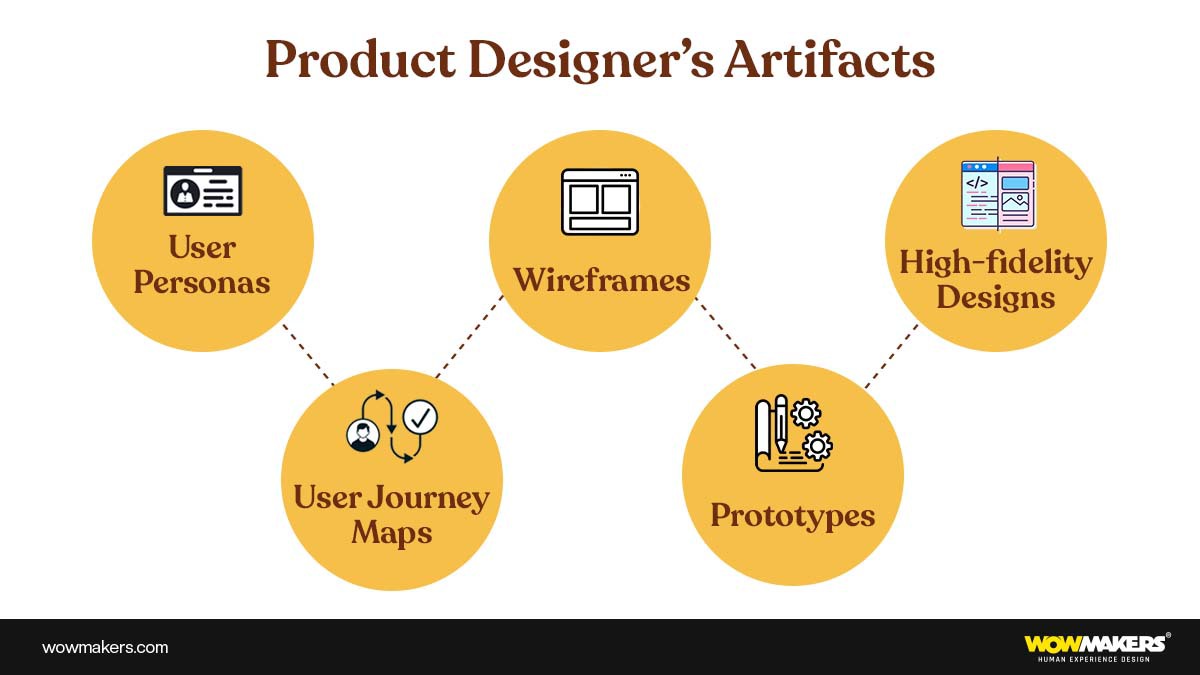
Making design decisions visible in artifacts (like wireframes) lets other people understand the context behind each choice and give more feedback.
As part of their jobs, product designers may have to deliver things like, but not limited to:
User Persona
User personas assist in better understanding users’ wants and needs. Product designers must first research their users to understand who they are to create a user persona.
After that, they start making a profile of the user, including their age, job, and way of life. This information will help the team better design a product that appeals to the users.
User Journey maps
Product designers must understand what users want, develop solutions that meet those needs, and then test them repeatedly to ensure they work. They must also be able to transparently explain their designs to stakeholders and users. They work with different stakeholders to identify pain points and opportunities and create a prototype that addresses these issues.
Wireframes
The product designer’s responsibility is to create high-fidelity mockups based on the wireframes to show how the solution might look and function.
A wireframe is a picture of how a website or app will be laid out. It sets up a page’s basic structure, and functionality before the visual design and content are added. It’s an essential part of interaction design, and it helps ensure the page is easy to use and gives the user a good experience.
Prototypes
A prototype in UX is a dummy or simplified version of the actual product. It is used to see how well a proposed design works if it is possible, and how people feel about it overall. Prototypes can be as simple as drawings on paper or as complex as a fully functioning website or app.
Generally, prototypes are used in moderated sessions with users to get feedback on how well the design works and to gather suggestions for improvement. At this stage, getting information and figuring out problems will help make the solution easier.
High-fidelity Designs
The mockups in UX provide a blueprint for the final product. They talk about layout, color, font, and all the other small details, right down to the last pixel. These mock-ups can be used to get feedback from stakeholders and users to help determine if the proposed solution is effective.
Product Designer: Remuneration, Skills, and More
A product design job can be gratifying!
The product designer’s job is to create products that are both functional and appealing to the eye. To get the product designer job, one must have excellent design skills and a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and materials. Product designers must also be able to think creatively and have an eye for detail.
How to become a product designer?
To become a product designer, you can take the following steps:
- The product designer position requires a high school diploma or GED, as this level of education provides fundamental knowledge and skills applicable to virtually any occupation.
- Some product design employers demand a bachelor’s degree in engineering, marketing, graphic design, or another related discipline. A bachelor’s degree can help you stand out from other applicants, even if a company doesn’t demand one for this position.
- Before pursuing the product designer role, Learn how to use industry tools and acquire soft skills like management and teamwork.
- Explore marketing, business, customer service, or problem-solving and communication opportunities. These jobs can teach you how to understand and meet customer goals, solve design problems, implement your process, and help companies reach their sales goals.
- Creating a portfolio allows you to demonstrate your expertise and skills as a product designer to potential employers.
- Read up on the latest developments in the industry.
- Determine the skill gaps in your arsenal. Consider taking UX design courses such as the Google UX Design Professional Certificate, where you can create a professional portfolio, engage with digital design tools, and master the fundamentals of user experience (UX) research.
Salary of Product Designers ( India, the US, and the UK)
Product designers’ salaries depend on their experience level, company, and where they live. Generally speaking, product designers earn a decent salary. In India, for example, the median salary for a product designer is around Rs. 11 lakh per year. While the average salary in the United States is $75,584, it is £51,429 in the United Kingdom.
Conclusion
Product designers are driving the future of design and user experience with their creative problem-solving skills. Designing anything, from websites to mobile apps, requires a lot of creativity and the ability to come up with solutions that go beyond what is already known.
A great product designer can take any idea for a digital product and turn it into reality.
FAQ’s About the Product Designer Role
#1) Are product designers paid well?
Of course, An established product designer with 5-9 yrs of experience can bag around $80,000 – $110,000 annually. Some companies provide double or triple salaries if you feel this is low. However, skills matter.
#2) Is product design a stressful job?
That depends on how you could handle stress. It doesn’t matter if you are a part of an organization or a freelancer; you always have to keep up with expectations, quality, and deadlines like any other job. So it’s evident that there will be stress. The UX design process is iterative and agile, and there will be a repetitive cycle in approving your work. Also, stress usually depends on your skills, the organization, your teammates, and many other things. in short, that bone-crunching stress you are afraid of is subjective.
#3) How to Get a Product Design Job Without Experience
Engrave this word in your brain, portfolio! work on some kick-ass projects that will showcase your skill. You will be considered for the role if they are too hard to avoid. Also, do not assume that the designs are good. Seek peer and expert review in this matter.
Contact famous designers through Linkedin and ask them to leave a comment on your work. If you think that you lack specific skills, work on them. Also, try to get acquire technical skills in using industry-leading tools. If you need assistance, attend boot camps and online courses. Certifications always add significant value to your candidature.
#4) What is the difference between UX and product design?
The goal of each type of design process is what sets product design and user experience design apart from one another. While the process of product design prioritizes the product’s viability from a financial perspective, UX design will emphasize the product’s utility for its intended audience.
#5) What should I study to become a product designer?
If you are looking for budget-friendly options, online courses are the best way. However, many good books are available to study design and UX concepts if you wish to dive deep. UG and PG courses are available if you want more of an academic study style.
#6) What is an example of product design?
Everything you see has been designed and manufactured to address specific problems. From the mobile phone to the clothing you are wearing now, it’s all designed by someone or a group who identified the need and addressed it.
Any product successfully managed to solve an issue is a good product. Let’s use the design of the Sony Walkman as an example here. It was released in the year 1979. Even though There were several different types of portable tape players on the market, none were designed to be used by a person on the go. The invention changed the way humans hear music and the music industry forever.






