Have you ever encountered a website or app with a great design that was challenging to use? Or maybe one that was easy to use but looked terrible? This is the difference between UI and UX. Both elements are essential for creating an effective website or app, but they play different roles. Let’s explore how UX and UI work together.
UX and UI Designs: What’s the Difference?
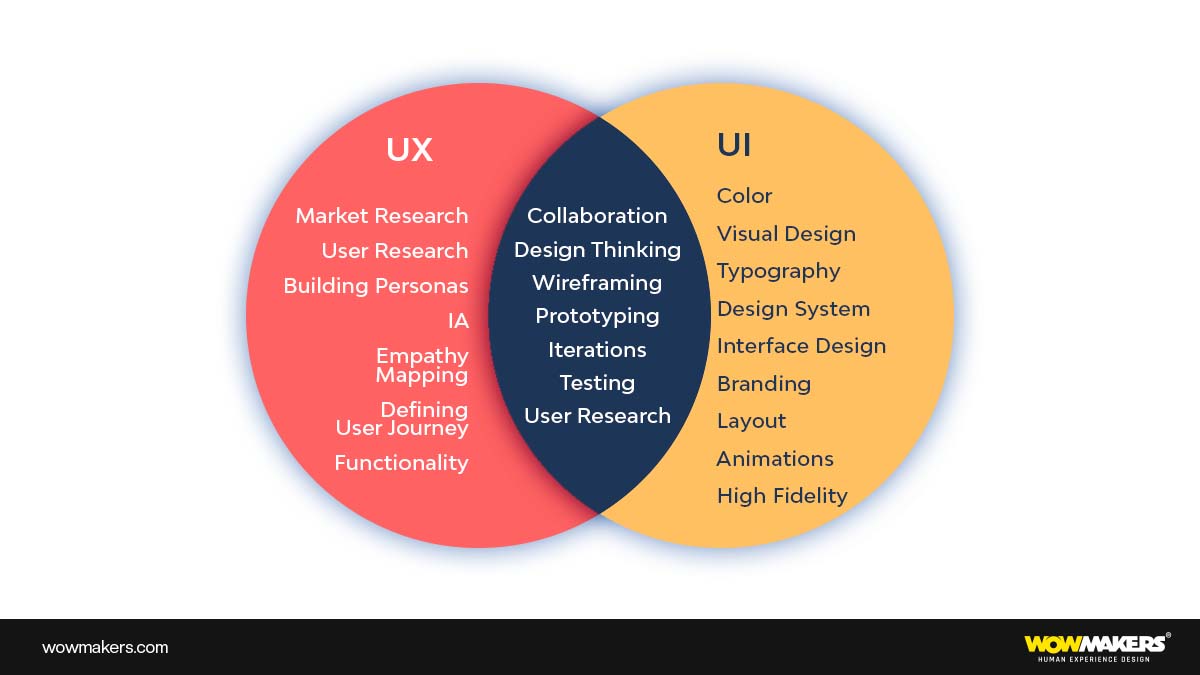
The difference between UI and UX can be explained using the analogy of driving a car. UX is like the overall design and chassis of the vehicle, such as the engine, brakes, fuel tanks, etc.
It’s the key to ensuring an enjoyable and safe ride. UI, on the other hand, is analogous to the interior of a car: its shape, colors, textures, materials, and any other details that make it comfortable and aesthetically pleasing.
While UX focuses on functionality and safety, UI emphasizes style and comfort. It’s also important to remember that both are equally important for a pleasant driving experience: a car with great UX but poor UI will not give you a good experience, just as a car with great UI but poor UX won’t be very reliable or practical.
What is UX Design?
User experience design (UX) focuses on how users interact with a product or service. It includes researching the user’s needs, goals, feelings, and frustrations when interacting with your product.
This research informs design decisions like layout, content organization, navigation structure, interactions, color scheme, and more. UX design aims to ensure users can accomplish their tasks quickly and efficiently while having a positive experience.
Roles and Responsibilities of UX Designer
- Understand user needs through research and interviews: UX designers must understand the needs and motivations of users to create an effective design. They should conduct interviews, surveys, and other forms of research to gain insights into their target audience.
- Develop user flows, and journey maps: UX designers must analyze the data they have collected to develop user flows that map out how a user might interact with a product or service. They should be able to identify areas where there may be confusion or a lack of clarity for the user.
- Create wireframes and prototypes: UX designers must use their research to create wireframes that depict user interface elements such as menus, buttons, input fields, etc., and interactive prototypes that demonstrate how the final product will function.
- Conduct usability testing: To ensure that their designs are practical, UX designers need to conduct usability tests, which involve presenting tasks for users to complete while observing their behavior to find any areas for improvement.
- Analyze results from A/B testing: UX designers also review data from A/B tests to determine which design works better for users. They should be able to make recommendations for changes based on this data.
- Monitor customer feedback: Finally, UX designers must continuously monitor customer feedback to understand how users feel about their products or services after launch and identify any potential issues or areas for improvement.
UX designers may make better-informed judgments based on genuine user feedback and reliable data if they do research at every stage of the design process.
Research also allows designers to identify hidden problems early on in the process and make improvements before it’s too late, saving time and money in the long run.
What is UI Design?

User interface design (UI) focuses on the visual elements of a product or service, like typography, layout, color palette, icons, and illustrations. Effective UI design helps build trust between the user and your product by making it look visually appealing and easy to understand. A good user interface (UI) makes it easy for people to use your product by clarifying their actions and how they can be taken.
Roles and Responsibilities of UI Designer
- Designing user interfaces that are visually attractive, highly intuitive, and consistent with a product’s overall brand identity
- Creating prototypes and user interface (UI) ideas for digital products like websites, mobile apps, and software programs
- Creating graphics, icons, logos, and product features using design tools like Illustrator and Photoshop
- Crafting responsive designs that seamlessly adjust to different screen sizes and platforms
- Working with user experience designer to ensure that the interface can meet user needs
- Creating interactive elements like buttons, menus, drop-downs, forms, and other custom controls
- Collaborating closely with developers to ensure a consistent design across all platforms by verifying the implementation of designs into front-end code
- Keeping up with the latest trends in user interface design for mobile devices so that they can be used to guide the development of app features.
- Testing proposed changes to improve usability and ensure browser compatibility.
The Role of Research in UI Design
Research plays a vital role in UI design. It helps ensure that user interfaces are made with the needs and expectations of users in mind so that the end product works well and is a success. Research activities can include:
- Analyzing user research results to understand the target audience, their needs, and what they expect from the design
- Identifying color palettes, patterns, fonts, and other visuals that will work best for the project
- Performing competitor benchmarking to learn which UI components other companies in the same industry use and what works better than others
- Using data-driven insights to create an optimized interface that meets users’ goals
- Before launching, prototypes should be tested with real users to assess usability issues.
- Gathering feedback from stakeholders to make sure designs meet set objectives.
By basing UI design on research, designers can develop solutions that get the desired results while meeting user needs. This ultimately leads to more successful products and experiences.
How do user experience design and user interface design work together?

UX and UI work together to create a seamless user experience. Here are some of the ways they collaborate:
- UX focuses on how easy it is to use a product, while UI emphasizes the attractive and aesthetically pleasing interface.
- UX looks at navigation and flow, trying to make sure users can easily navigate from one page to the next, whereas UI works on creating an enjoyable visual look and feel for the product.
- To ensure an adequate design, UX designers research best practices for user interfaces and create prototypes for testing. In contrast, UI designers focus on crafting beautiful designs that meet users’ needs and expectations.
Both disciplines must be aware of usability considerations when designing a product; for example, UX designers must consider readability when laying out content, while UI designers must consider how fonts and colors affect user interaction with the product. - Developers bridge both disciplines using front-end technologies like HTML/CSS to ensure the aesthetics of design (UI) and usability (UX) are accurately implemented in the final product.
In the end, UX and UI design work together to make a successful digital product that meets aesthetic and functional criteria.
When these two fields work together, users can easily interact with a website or app without getting frustrated or confused by its complexity or lack of visual appeal.
Importance of Good UI/UX Design
UI/UX design is becoming increasingly important as businesses try to give users unique and exciting experiences. Without good UI/UX design, websites and apps can be hard to use, slow to load, and hard to move around in. This can make the user’s experience terrible.
Good UI/UX design considers the user’s needs and ensures that the website or application meets those needs efficiently and intuitively. It also focuses on making good designs, grabbing the user’s attention, and keeping them interested. It also helps make a good impression of the brand by ensuring that all elements align with the company’s brand identity.
Furthermore, UI/UX designs help optimize content for mobile devices, making it easier for users to access information while on the go. So, good UI/UX design not only makes something easier to use, but it also increases engagement, makes customers more loyal, and boosts sales.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between UX and UI design is essential for creating effective digital products people love using. When used together correctly, UX and UI can create a fantastic user experience that encourages people to use your product repeatedly.
A great example of this combination in action can be seen in streaming services like Netflix or Spotify, where UX and UI have been carefully thought out for users to find exactly what they need quickly and enjoy their time using the service overall.
So if you’re looking for ways to improve your product’s user experience, consider investing time into understanding and leveraging both disciplines properly! Consider taking UX design courses like the Google UX Design Professional Certificate. You can make a professional portfolio, use digital design tools, and learn the basics of user experience (UX) research.
FAQs about UI and UX
Does UI UX require coding?
Coding is a skill as a designer it would be beneficial for your career. Also, coding can help you communicate well with developers if they have messed up your design. Not just that, but understanding the developer’s plight is also one of the advantages of coding. If you are wondering which language you should learn, understanding coding concepts such as HTML, Java, and CSS would also be beneficial for design.
What is easier, UI or UX?
It depends on what you would like to learn. Visual UI learning is easy to understand if you have a graphic design background. However, a clear understanding of design principles is necessary. UX is more about researching and practical tests to determine what users will like. Easy is based on perspective; it depends on what you like and not.
Is UX frontend or backend?
User Interface or User experience designers decide how users will see the application: appearance, button placement, functionality, etc. On the other hand, front-end developers are responsible for web client-side development. Unlike the UI and UX specialist, the Front-End developer makes the interface work.
UX vs. UI: How do you work out which is a better fit?
It will all boil down to your area of interest. The thing is, even areas of interest are subject to change over time. Regarding career aspects, both UI and UX have merits and demerits. If you would like to learn both, you get a competitive advantage.