As a business owner, it’s crucial to understand how your customers interact with your product or service and their experience from beginning to end. In short, it’s essential to define your SaaS customer journey from the very beginning.
In this blog, we’ll explore the various stages of the SaaS customer journey, from the initial awareness and consideration phases to the decision-making process and ultimately to the post-purchase experience.
By understanding each step of the trip, you can identify opportunities to improve the customer experience and drive customer loyalty. So join us as we take a deep dive into the SaaS customer journey!
What is the SaaS customer journey?
Recently, customers’ power to make decisions has been increasing substantially. Thus, a business can no longer rely only on its marketing department to determine what to do next. Because they can’t speak for all of your customers and frequently care more about the creative parts of product promotion than the truly satisfying customer wants.
With the advancement of technology and the vast array of channels presently available, it is challenging to keep up with every single consumer. This led to the development of the term “customer journey.”
The SaaS customer journey represents every customer interaction with your business at different phases, from onboarding to advocacy. You can group customers into stages to help your team determine the best action to achieve customer success. It can be challenging to maintain track of each customer individually.
SaaS customer journey maps are developed to help customers reach their objectives and get the most out of your services. The customer journeys give you an idea of the kinds of actions that your internal success team and customers will need to take, and each stage calls for a specific strategy.
If you think otherwise, have a look at these statistics.
- The Temkin Group estimated that organizations with yearly revenues of $1 billion might expect to generate an extra $700 million within three years if they spend on improving their customers’ experiences.
- Consumers are so fickle that 86% would abandon a brand after two negative encounters.
- After a more tailored interaction, 49% of customers have made a spontaneous purchase.
- Over three-quarters, (73%) of customers agree that CX influences their final decision.
- More than 96%of consumers say good customer service is essential to stick with a particular brand.
Benefits of SaaS customer journey
Since you gave the customer a voice and chose to listen to and understand them, a customer journey map helps your business and team become more compassionate—your focus and creation of a path map from their viewpoint help with the retention of your customers.
Your team and organization can consistently understand the needs and desires of the client, thanks to the customer journey map. The SaaS customer journey map solution makes it simple to access the customer’s journey across all platforms, making the customer’s response more quickly successful.
Understanding the usefulness of a chatbot for your website may be made easier for your business and team with the help of SaaS customer journey mapping. It helps you create new opportunities that increase your success rate. As a result, customers are more satisfied and have a better experience.
It anticipates consumer behavior with the help of data journey mapping, which gives your team and company a broad understanding of the customer journey and helps with problem-solving and problem prediction. The travel map facilitates and contributes to clients’ success.
Finally, mapping improves the team’s and the business’s general marketing success. Customer journey planning enhances customer experiences and helps the company succeed/increase sales.
Stages of SaaS customer journey
You may focus on what you want the customer to do at each phase or stage by being aware of the numerous steps in the customer journey for your SaaS company.
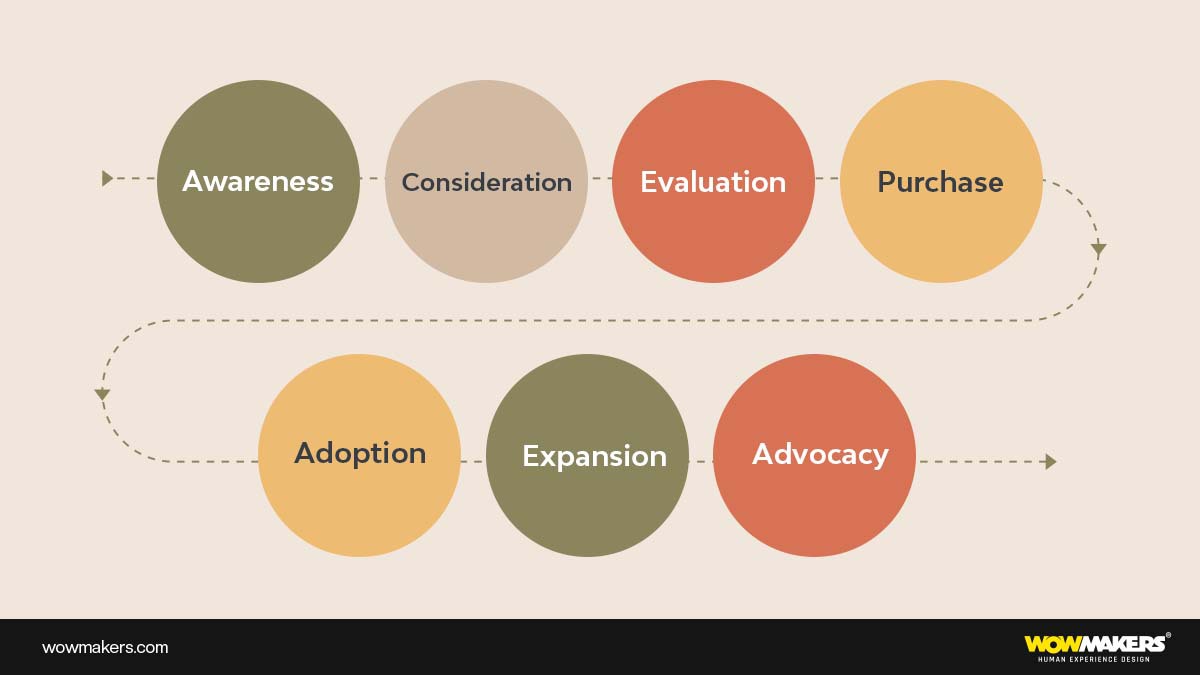
Awareness
Typically, the awareness step comes first in a client journey. At this stage, your customer either runs into a problem and starts looking for solutions, or they learn about your product for the first time (perhaps from recommendations from others or online reviews) and want to know more.
Here, you must ensure that your content is captivating and distinctive and explains how the product may solve the issues. Cast a wide net using techniques like advertising, SEO, events, social media, or a referral program.
Consideration
Here, the customer is looking more closely at the product or platform to see if the range of services or features will be able to solve their problem. Remembering this stage could take longer because the customer might need extra time to weigh all his or her options.
Suppose your SaaS company has a rich content center that includes blogs, webinars, white papers, case studies, and newsletters explaining how it can improve customers’ lives and solve their problems. In that case, things can get more straightforward for you.
Evaluation
Your customer is about to make a decision. They may need to choose between two well-liked platforms and choose to invest some time learning about and utilizing each one individually.
A product-led strategy will help your SaaS company in this situation. The customer can use a freemium model or sign up for a brief free trial to thoroughly research your products.
Purchase
Their choice for the following action is your product. The payment was processed, and they are now officially a customer.
However, don’t get comfortable just yet—the SaaS customer experience is only getting started.
Adoption
Here is where a simple onboarding process becomes crucial for your SaaS company. We’re talking about giving users the finest first-time login, sign-up, and welcome email experiences possible. All of them will make it simpler for people to accept your goods.
Expansion
Your customer can now view your product as a regular part of their daily lives after using it. But maybe most importantly, it has taken care of their initial problem. This phase’s objective is to enhance your customers’ use of your product.
Advocacy
Customers are considered loyal if they adore the product, keep using it, and interact with the business. They must join a referral program, endorse the product to their coworkers, or spread the word on social media to become an advocate.
How to improve the SaaS customer journey?
By forcing you to think about how your customers engage with your brand rather than how you imagine they do, customer journey mapping has the advantage of helping you understand their motivations.
The following essential customer journeys are essential to understand since they aim to address problems that many SaaS companies encounter:
Lead nurture
By implementing a lead nurturing plan that includes lead qualification criteria, you can create a lead hierarchy and choose which leads to focus on first.
Trial conversion
SaaS companies provide a free trial or freemium account option to convert these people into paying customers.
Onboarding
When a consumer decides to join up for your product, the race is on to get them set up and utilizing it as soon as possible so they may experience their joyous moment.
Customer retention
The needs of the clients are your primary concern. Communicating the product’s value, keeping customers motivated, and having a quick response time if something goes wrong are three crucial components of your customer retention strategy.
Avoiding trial abandonment and churn
Let’s face it; it hurts when a trial user chooses not to convert or when a current user chooses not to use your SaaS product any longer. “Churn” is one of our least favorite terms.
Unfortunately, churn happens frequently in SaaS businesses. Churn cannot entirely be eradicated, but it can be lessened. Hence it is crucial to plan out trial abandonment and churn reduction techniques.
SaaS Customer Journey Metrics
Various metrics can help you to access your customer journey:
Customer lifetime value
The total profit a company might expect to make throughout a specific customer relationship is known as customer lifetime value (CLV).
Your customer success operation has an impact on two crucial performance measurements, which are combined to produce customer lifetime value:
- Annual revenue for each client
- The typical length of a client relationship (in years)
Repeat purchase rate
Your repeat purchase rate (RPR) reveals the number and percentage of customers making additional purchases due to a profitable customer success project.
Customer retention rate
Your customer retention rate is the proportion of current customers you kept in a given time frame. How many customers stick with you over a month, quarter, or year?
Customer retention cost
The customer retention cost (CRC) measures the cost to your business of keeping each customer.
Churn rate
Measuring your churn rate fundamentally involves looking at retention from a new perspective. In contrast to retained customers, churn measures the number of customers you lose over time.
Net Promoter Score
The previous customer success metrics we covered diverge significantly from the Net Promoter Score in several key ways (NPS).
The findings of an NPS survey are utilized to determine your Net Promoter Score. In a survey, a 10-point scale is used to gauge whether respondents would recommend (company or product) to their friends.
- Customers who respond with a number between 0 and 6 are considered “detractors.”
- Those who score 7 or 8 are considered “passives.”
- The responders who chose 9 or 10 will be referred to as “promoters.”
Customer Satisfaction Score
You can calculate your customer satisfaction score based on how customers evaluate their interactions with your business. Additionally, you have a lot of choices about the queries you pose to your clients, the grading system you use, and other factors.
Customer Effort Score
Based on the idea that customers are less likely to utilize your service or product if it requires more effort on their behalf, the Customer Effort Score (CES) is one of the more recent customer success indicators to gain attention.
You must consider consumer effort when assessing your performance in terms of customer success.
What is SaaS Customer Journey Mapping?
Customer journey mapping (also called user journey mapping) creates a journey map of how consumers connect with your brand. Through this activity, businesses learn to put themselves in their customer’s shoes and view their business operations from their clients’ perspectives.
You can discover common customer issues and solutions using customer journey maps. Every prospective consumer touchpoint, including a website, social media channels, and interactions with the sales and marketing teams, is first conceptualized.
Following that, customer journeys across these various touchpoints are created for each consumer profile. A customer journey map should include the customer experience at each touchpoint. This can include what the customer needs to do and how your brand will respond.
How to visualize customer mapping?
To visualize customer mapping, you can use tools that visually represent the interaction between a brand and its audience. It all revolves around the many stages, from the customer’s initial exposure to the brand and product to the possibility of their initial purchase and retention.
It also entails paying close attention to how customers interact with your brand and merchandise and figuring out the many stages of their interests, wants, and purchase barriers.
Everything is evident from their first point of contact (interaction) with your brand to why they decided to buy a specific product from your company’s brand.
Customer Journey Mapping Example
Here are two examples of what we did for our clients
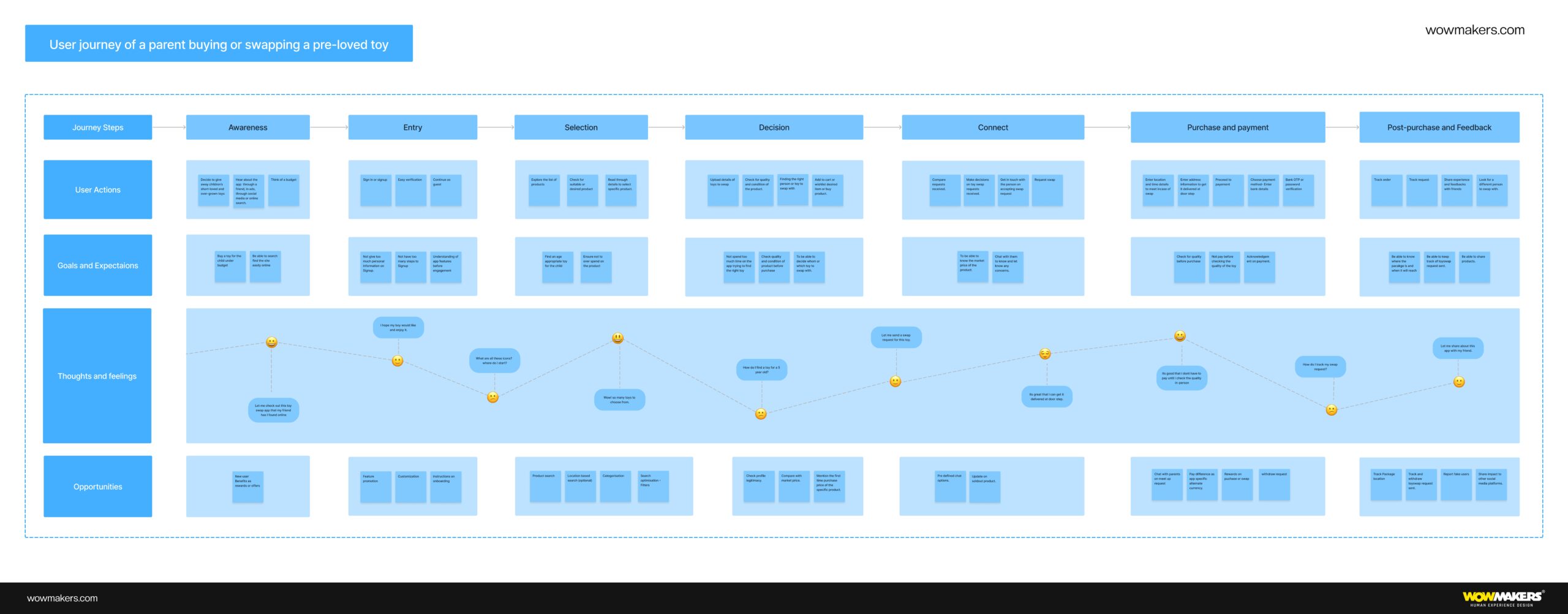
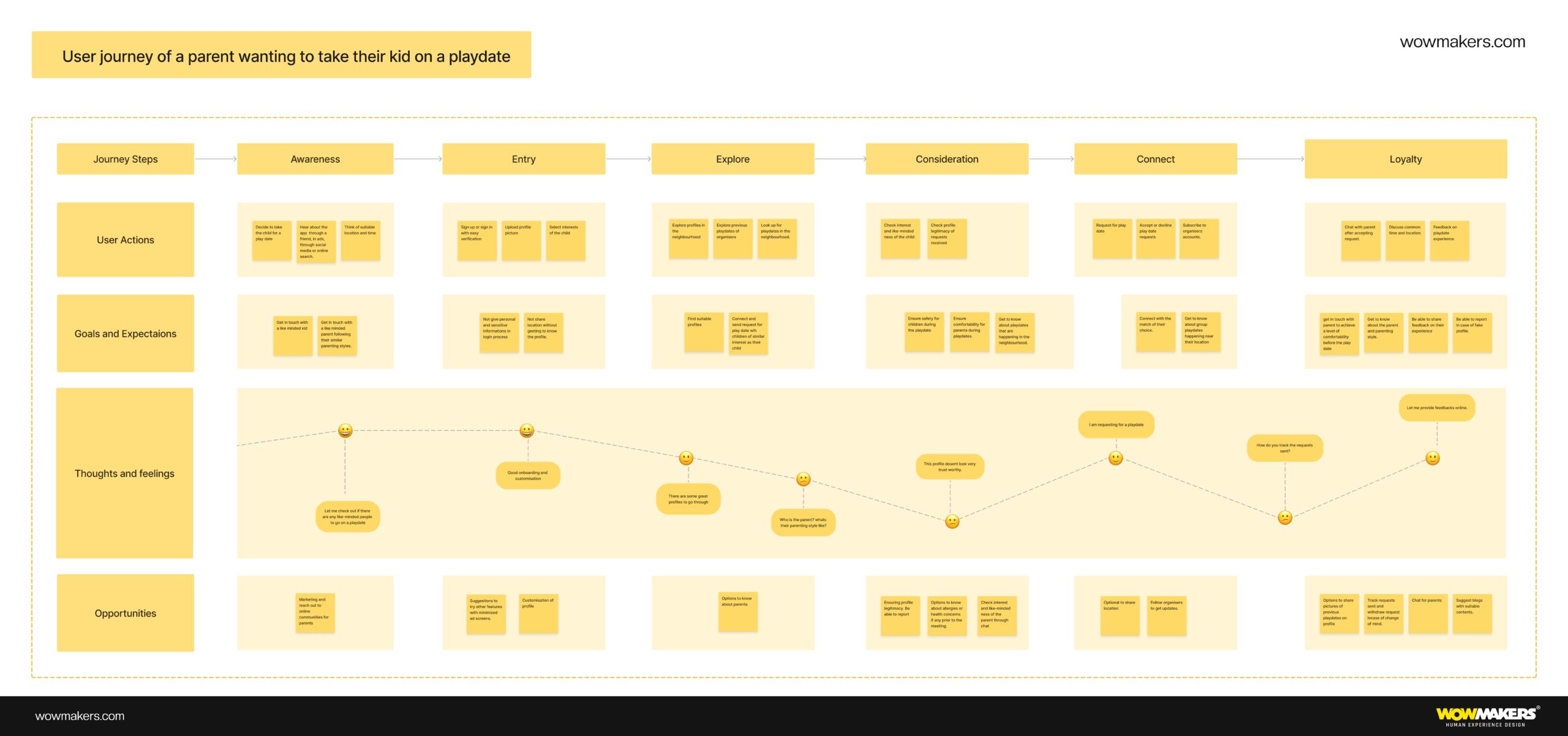
Customer Journey Mapping PDF Example 1
Customer Journey Mapping PDF Example 2
Why is journey mapping critical?
Now that we are familiar with journey mapping, we should understand the reasons for using it.
Increases customer retention by considering post-purchase experiences in a well-designed customer journey map. This information will aid your comprehension of client churn. Once you are aware of this, you can work to strengthen both your strengths and your weaknesses.
- Increases the effectiveness of your marketing initiatives: By understanding customer decision-making processes and the platforms they like to use, you can create campaigns that precisely aim to satisfy their demands on those platforms.
- You can better understand your customers by being aware of their touchpoints, which will also help you understand how your buyer personas progress through your conversion funnel. You can now tailor your marketing strategies as a result.
- Customer journey maps enable you to improve the client experience across all contact points.
Customer journey maps assist your clients in more successfully achieving their goals. - It provides vital background data on who your customers are. Customer journey maps shed light on who your customers are, their challenges, and where they run into roadblocks.
Journey mapping puts your company in a better position to boost performance in general as your attention shifts from the organization to the customers.
What are the elements of journey mapping?
Creating a customer journey map is one of the most effective ways to comprehend how customers interact with your organization. You will be able to deal with any issues by identifying potential trouble spots or confusion by outlining each step of this journey. Let’s examine some of the main driving forces at play.
Focus on Customer Experience
The customer experience comes first in customer journey mapping. The best tactics focus on a specific customer group and are supported by data rather than speculation. Customers’ interactions with your brand and their experiences are among these factors.
Objectives that are specific and doable
Journey mapping must serve a specific function and provide information that can be used. Include all of your findings, whether favorable or unfavorable, and then look for any relationships between them and your customers’ actions, goals, and expectations.
An omnichannel CX viewpoint
Many firms operate in silos, with each team focusing on a particular set of touchpoints or channels. On the other hand, customers don’t consider these channels since they consider every part of their journey, including all their encounters with companies. Therefore, successful customer journey mapping should consider the complete CX – all customer interactions with the business — regardless of which team oversees which channel.
Informational cues and crucial metrics
Qualitative research using modest sample numbers is the primary source of information for a functional map. However, quantitative data might add to the validity of the results and provide additional information.
You can develop a set of KPIs that can be used throughout the process by utilizing quantitative research (or only certain portions of it). Thanks to the net promoter score and other customer satisfaction metrics, your map can be utilized to evaluate how well you’re doing with CX improvements.
Level-up those graphics
A customer journey map already offers a visual representation of the CX. Still, you might want to take it a step further to make it more practical by organizing it in a way that is both appealing to viewers and allows you to add more data as you gather it. You might even consider creating several versions for various people according to their responsibilities.
What are the 5 A’s used for Journey mapping?
The 5A’s used for building customer journey maps are:
Aware
The Aware stage of the customer journey is when a potential customer first becomes aware of a business.
Appeal
A potential customer knows a brand’s or company’s benefits and finds it intriguing.
Ask
The potential customer can then research the company’s products and services to compare them to the alternatives they are considering. They could call, email, or use the chat feature on the company’s website, or they could do both. The potential customer is now curious about the specific features and benefits of the product they have inquired about with the company.
Act
At the Act stage, the potential consumer purchases the company. This purchase could be made in a single transaction for good or through a subscription model where users pay a fee for a service they use frequently.
Advocate
The customer now promotes the company as a result of their purchasing experience. They might post company content on social media, tell their friends and family about the company, and offer endorsements or customer reviews for the product or service.
Tools used for SaaS Customer Journey Mapping
As your product and service evolve and expand, you’ll need to provide your customers with increasingly specialized experiences. Examining everything, including goals, outcomes, and the emotions resulting from working to reach those outcomes, is required. This enables your team to locate potential friction points, eliminate them with more straightforward transitions, and increase conversion. You can immediately start creating the ideal customer journey map with these tools.
Miro
Using Miro, you can choose from various templates, including kanban boards and customer journey maps. It is intended to help users get up and running as soon as possible.
UXPressia

UXPressia is a system that was created exclusively for the customer journey and is focused heavily on improving the customer experience. Many templates are available from them, including ones for customer journey maps and even onboarding new team members.
Smaply
Another specific tool for the customer journey is Smaply, which can help you identify possible pain points and crucial moments in the trip flow. They provide path mapping for your customer base and help you identify personas and team influencers at each stage of the journey.
Here are a few more examples of technologies used for customer journey optimization
- A data management platform (DMP) can collect, organize, and integrate omnichannel consumer data to enable targeted marketing actions and enhance the customer journey.
- A CRM system that uses the Journey Builder module to build individualized journeys across channels engages customers at every touchpoint (email, mobile, advertising, social networks, etc.).
What are the steps of journey mapping?
Journey mapping is the most crucial aspect of every business; here are the steps involved in journey mapping:
Step 1: Identify Your Objectives
Why are you doing journey mapping? What goals are you trying to achieve with this mapping? What kind of experience will it consider? Which types of customers will it serve?
Consider the who, what, and why very carefully since they will guide the rest of the plotting process.
Step 2: Make a list of customer personas.
You cannot follow a customer’s movements if unaware of their identity, preferences, issues, and goals. One of the best ways to create your customer personas is to research and test actual customers who have interacted with your brand.
Step 3: Discover Each Touchpoint
The locations where customers can interact with you online and on your website are known as touchpoints. Putting something in your shopping cart, leaving a comment on a social media post, checking your email, etc.
Step 4: Select the Map Type.
Your choice of customer journey map will depend on your objectives. The most common kinds of maps are:
- Current State: The most common type of map, the current state map, enables you to observe the present-day actions, ideas, attitudes, and feelings that your clients are experiencing as they interact with your company.
- Day-in-the-life: This illustrates your customer’s entire day. It describes their daily activities and interests, regardless of whether they require interacting with your business.
- Future State: These represent the activities, concepts, behaviors, and feelings you predict your customers will have when they interact with your brand in the future.
Step 5: Make a map of the customer journey.
You have focused on a particular clientele and are familiar with them. It is now necessary to map out the client journey step-by-step. Just focus on what you’re doing right now. What actions do your customers take, and when?
Step 6: Consider the client experience.
Walk through the customer journey you mapped out in step five as if you were your customer. The most crucial step is this one. Note any uncomfortable circumstances, such as when you don’t get the required knowledge or experience. Analyze your actions to find out why they feel natural.
Now that your customers’ needs are met, you may concentrate on those areas. From there, your product can be modified to ensure brand engagement.
Conclusion
Knowing your clients is crucial if you want to keep running your SaaS firm. Spend time taking the steps necessary to turn customers into your advocates.
Establishing an expert SaaS customer journey can help you achieve your goals and ensure that your customers speak of your brand and become its brand ambassadors.
After all, customers are king!