Product design vs. UX design. What does the word versus mean here? Is there a competition or something going on?
It’s just common internet slang used to differentiate. Let’s look at the primary definition of Product design and UX design.
Product Design: To ensure that the finished product meets the needs of both customers and the business, it has a product design.
UX Design: As the name suggests, here, customer interaction is given more prominence when it comes to designing a product.
Then, what makes product design and UX design different?
Product and UX design play a significant role in building up your user’s trust and faith in you.
Let’s get started by understanding both of them separately.
What is UX Design?
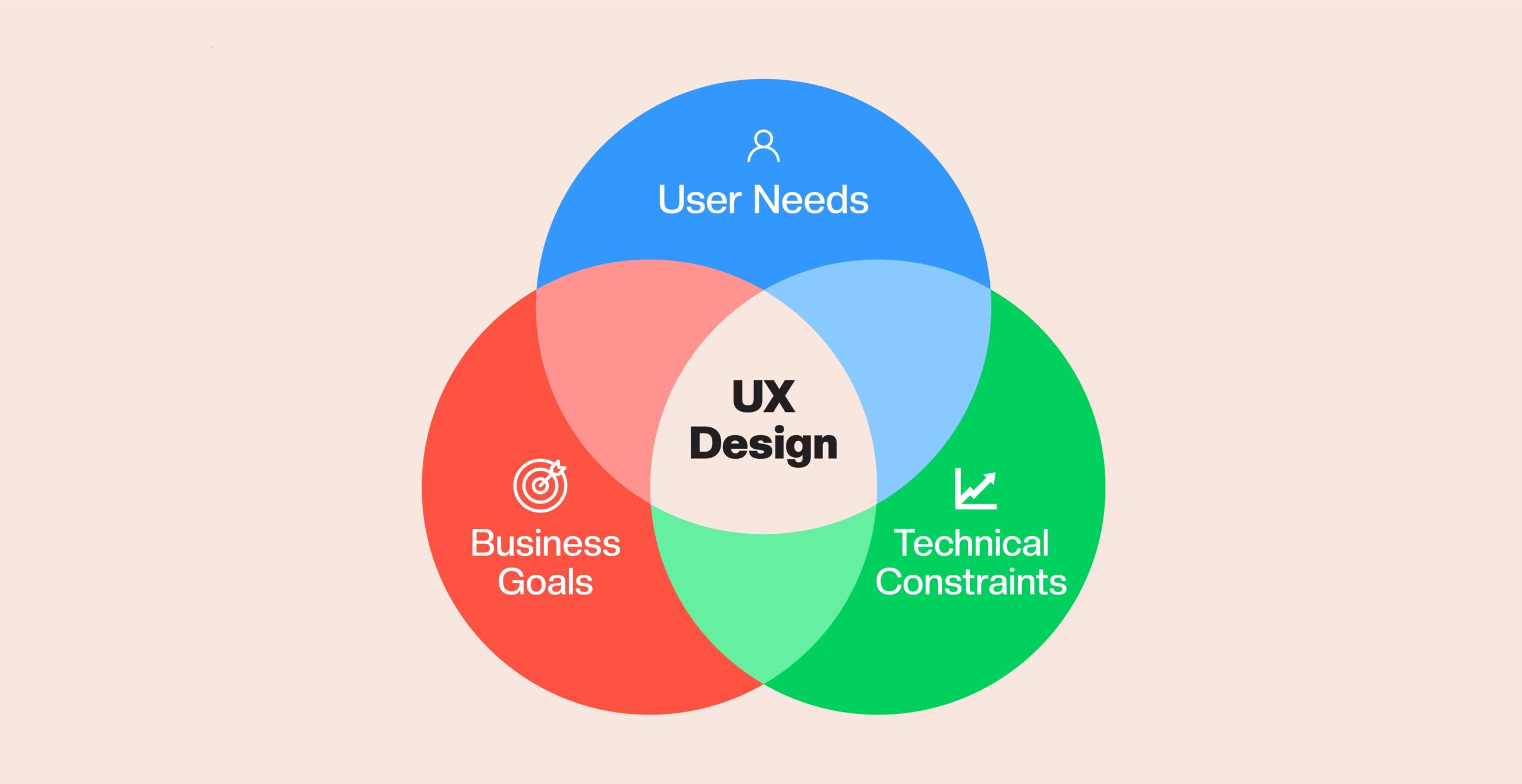
User experience, or UX, refers to any interaction with a product or service. Besides considering how easy it is for a user to accomplish the desired task, UX design also considers the important factors influencing this experience.
UX design aims at producing products that people will find entertaining and easy to use. User experience design focuses on meeting users’ needs while being careful not to interfere with their ability to appreciate the product as a whole fully.
You should include anything from how an object feels in your hands to how easy it is to complete an online checkout.
The purpose of user experience design is to provide users with an intuitive, practical, relevant, and overall enjoyable experience. UX designers combine market research, product development, strategy, and design to create seamless user experiences for goods, services, and processes.
Establishing a relationship with the customer help the company better understand and fulfill their needs. The focus of UX Design is on the user’s experience and needs.
The UX design can answer your questions like
- Are customers happy with this product?
- What advantage does this product or feature provide for our users?
- How can the usefulness of this product be improved?
Who is a UX Designer?
UX Designers, when creating the design, they put a focus on user interaction, making efforts to improve the product’s usability and accessibility continually.
A UX designer will oversee the entire design thinking process, from research to ideation, always keeping the user’s demands in mind. The role requires user testing, prototyping, and adopting the user’s viewpoint. In other words, it is their responsibility to ensure that the product is as user-friendly as it is practical.
What is Product Design?
Designers use a process known as product design to combine consumer needs with business goals to assist firms in producing consistently profitable products. The process of conceiving, creating, and commercializing a product is known as product design. Product design focuses more on business requirements than that on the user experience.
Product designers help their businesses and service users by enhancing the user experience in the solutions they offer by developing products that are sustainable for longer-term business demands.
The main distinction between product design and UX design is the purpose of each design process. The focus of Product Design is the entire interaction between the customer and the product.
Modern product design increasingly includes digital products, even though it is frequently associated with physical objects (such as websites and apps).
The product design can answer your questions like
- How can we make this product less expensive?
- Does this product help the company achieve its short- and long-term goals?
- How will this product appear in two years?

Who is a product designer?
Many people still find it difficult to comprehend the role of a product designer, sometimes even including product designers themselves.
A full-stack designer, or “jack of all trades” designer who handles UX, UI, coding, project management, and problem-solving, is comparable to a product designer. The job of a product designer is typically highly flexible. In the early stages, a product designer’s main job is to come up with solutions to any problems that might come up.
To deal with these problems, product designers will put together groups to help find solutions, make several test plans, build wireframes, and do rounds of A/B testing. A product designer will work with the marketing teams and help the developers during the launch process to ensure that the brand and the product are in sync.
In a word, they are the product’s guardians. They make sure it is the most useful, relevant, and affordable product possible and that everyone is happy with it.
A Day in the Life of a UX Designer
A UX designer’s day can be pretty exciting because it involves so many different duties and jobs. These jobs can be fun sometimes, but they can also be challenging and tiring at other times. Depending on the UX design procedure, any of the following tasks might make up a UX designer’s typical day:
- Conduct discussions with corporate stakeholders to comprehend the aims and business plan and develop a UX strategy that is in line with the primary business goals
- Carrying out, overseeing, or procuring user research while combining concepts from UX research analysis to produce information that is relevant and valuable
- Creating workshops
- Making user experience deliverables, such as user flows, empathy maps, UX personas, and other assets, and producing mockups, prototypes, and wireframes
- Establishing and maintaining a style guide to develop the guidelines that should be followed for all UX projects
- Testing designs to ensure their accuracy and working closely with UI designers and developers to finish the overall look, feel, and behavior of the product
A Day in the Life of a Product Designer
A product designer’s day can be pretty thrilling, involving a lot of varied tasks and responsibilities. These tasks can sometimes be fun, but they can also be very daunting and tiring. Some of the routine functions performed by product designers include the following:
- collaborating with engineers, designers, and other team members to develop and implement a product.
- Creating documentation with team members, identifying trends, and creating style guides.
- development, testing, and prototyping of software
- Customers are surveyed to find out what objectives they have for a product, and team members collaborate and attend meetings to improve processes.
Skills required by UX designer and Product Designer
UX and product designers have distinct job profiles, as do their responsibilities and required skills. Though there may be some skills that are the same for both job profiles, a few of them vary and are the main distinctive factors for them both.
Some of the essential skills required by a UX designer are
- Interpersonal, collaborative, and communication skills
- Empathy
- Curiosity and continuous learning
- Critical thinking
- Wireframing and prototyping
- UX writing
- Visual communication and UI
- User testing
- Business acumen
- Research skills and analytics
- Customer service
- Coding and development
Skills product designers must have
- Creativity
- Attention to detail
- Decision Making
- Teamwork
- Communication
- Project Management
- Time Management
- Coding
- User testing
- Copywriters
- SEO
- Marketing
- Analytics
- Business acumen
- Research skills and analytics
- Customer service
The career path of UX Designer and Product Designer
UX designers and product designers both advance with a more incredible experience. Their career path is quite lucrative and ensures a unique, thrilling career.
As their knowledge and skills increase, UX designers may seek careers in various fields.
-
UX management
As UX designers get better at their jobs, they usually get more responsibilities and chances to lead projects. This may eventually lead to senior positions like chief experience officer or vice president of UX and managerial positions like UX manager, UX director, or creative director.
-
Advanced UX positions
The possibility for professional advancement exists for UX designers. As a result, you might eventually land jobs as a senior, lead, or principal UX designer.
-
Freelancing
UX designers favor the freelance option for many reasons, including the ability to set their own hours and select their own clients.
-
UX consulting
A UX consultant is a person who helps an organization’s business strategy and design move forward by making suggestions based on user experience principles.
-
UX Specialist
If you find that you are drawn to particular aspects of UX design, it can be a good idea to explore making a lateral shift to a position in a related industry. UX researcher, UX engineer, and UX writer are some options you can try for.
A product designer’s career path advances as his experience level rises.
-
Associate Product Designer
It is an entry-level position. To do their job, product designers in this position must rely on product managers or other product designers with more experience.
-
Product Designer
The next step on the career ladder is being a product designer. Every step of the creation process involves the involvement of product designers.
-
Senior Product Designer
The next step on the professional ladder is to become a Senior Product Designer. The job of a senior product designer is to work with customers to find out their needs, wants, and preferences so that new products and services can be made that follow the rules and policies of the company.
-
Principal Product Designer
The next stage on the professional path is to become a principal Product Designer.
-
Staff Product Designer
The ultimate goal of any professional journey is to become a senior staff Product Designer.
Roles and Responsibilities of UX Designer and Product Designer
The primary way that Ux Designers and Product Designers are distinguished from one another is by their roles and responsibilities. Here are the functions and duties of a UX designer and a product designer, which make it clear how the two positions differ.
The roles and responsibilities of a UX Designer include the following:
- Prepare for, conduct, and assess a study of competitors and users.
- Analyses of the data and qualitative observations
- Create user stories, personas, and storyboards.
- Create sitemaps and decide on the information architecture.
- Creating wireframes and testing prototypes for usability
The roles and responsibilities of a Product Designer include the following:
- Using information from internal teams and user research, establish design specifications.
- Analyze the possibility of improving a new product.
- Consider how a new product satisfies both market and customer demands.
- Observe market developments and business trends.
- Work together with other team members to ensure precise and consistent communication.
- Modify and change current designs to account for changing customer preferences.
- Work closely with product engineers to suggest enhancements for goods and procedures.
- provide cross-functional teams and senior leadership with product design concepts.
Salary differences between a product designer job and a UX designer job
Both product designers and UX designers have bright futures and lucrative salaries. Average salaries can vary depending on the location, sector, and years of experience.
UX designers in the US get an average salary of $115,743, while product designers make an average salary of $105,199.
Similarities between Product Design and UX Design
The most apparent resemblance between product design Vs. UX design is the utilization of the design thinking process. Both focus on product issues and have a customer-centric perspective. Both require some market research to make the product worth it.
UX and product designers often work with people from different departments, so they need to be good at communicating.
Not to be forgotten is that both designs need to know their users to be successful. Both UX design and product design employ a range of standard tools. For example, it’s common to use wireframing tools like Adobe and Sketch when making websites or apps. They may also share user mapping apps such as Lucid Chart and Featmap.
Product Design Vs. UX Design
Although product and user experience design frequently overlap in practice, they are distinct. The first one looks at the specifics of how a product is used, while the second one looks at the bigger picture.
Responsibility: User experience (UX) design is focused on what users want, while business considerations generally drive product design.
Product design requires more business knowledge to make sure that the final product meets the needs of the company. To make a product more user-friendly, UX design instead emphasizes the product’s interactive and visual elements.
Design Method: The objective of UX design is to improve a product’s user experience. Because of this, a major percentage of the duties performed by UX designers include developing interaction patterns and designing product user scenarios. Before using testing strategies (email surveys, A/B testing, etc.) to keep tabs on user behavior, they develop an interface prototype.
Product design, however, is more focused on achieving the “right” overall look and feel. Product designers look for market possibilities and consider how to position the product as a solution to customer problems, in addition to defining how individual components of the product should operate.
Skill Sets: Top-notch designing and problem-solving skills are necessary for UX and product design. There are a few minor distinctions in the skill set when discussing product design Vs. UX design.
Even though a UX designer’s job will be more about design, it will require more tact and business knowledge to design products. Product designers should be knowledgeable in UI design, graphic design, and user research in addition to prototyping tools, which UX designers should be more familiar with.
Tools Required: The tools that the designers use also contribute to their variances. Most of the time, they both use prototyping tools that come with the same design software. Additionally, product designers use sketching and mind-mapping tools, whereas UX designers use interactive and wireframe design tools.
Even though their core objectives are the same, the link between UX design vs. product design illustrates the distinctions between their operating procedures. They can both take care of your company’s demands.
| Product Design | UX Design | |
| Responsibilities | Product Design is driven by business considerations and necessitates more business awareness. | UX Design is focused on what users want. Places more emphasis on the product’s interactive and visual elements. |
| Design Method | Focused on achieving the “right” overall look and feel. | Improves product’s user experience |
| Skill Sets | Top-notch designing and problem-solving skills are required for Product Designing. | Top-notch designing and problem-solving skills are required for UX Designing. |
| Tools Required | Requires sketch and mind-mapping tools | Requires interactive and wireframe design tools |
Product Designer Vs. UX Designer
Here is a quick look into the differences between a product designer and a UX designer.
| Product Designer | UX Designer |
| Develops the design system | Develops the design system |
| Product Designer has the ability to work cross-functionally and communication. | UX Designer has the ability to work cross-functionally and communicate |
| Product Designer follows a user-centric approach | A UX Designer requires an understanding of InVision, Sketch, or another prototyping tool. |
| Engineering teamwork is a must for a Product Designer | Engineering teamwork is a must for a UX Designer |
| Creating desktop and mobile designs that are practical is the key skill for a product designer. | Analytical and logical thinking are key skills for a UX designer |
| Product Designer carries out user research | UX Designer carries out user research |
| Prototyping, designing, and wireframing are important for Product designer | Knowledge of company interface, UX, and graphic design is important for UX designer |
Myths Related to UX Design Vs. Product Design
When discussing these controversial ideas, there are several typical misunderstandings regarding product designs Vs. UX designs. Many groups have tried to figure out what the difference is. These groups are often put into the following groups:
- Despite similarities, product design includes additional elements. Many people believe that UX designers solely take the needs of the user into account, whereas product designers focus on both business objectives and user expectations. It’s untrue. Business needs have ALWAYS needed to be taken into account in UX designs also.
- UX design has evolved into Product Design. It is believed that UX design is getting evolved into product design. This is not true. This strategy has a weakness because not all experiences are products. Of course, whether that statement is accurate depends on how broadly you define “product.”
Final Takeaway
Product design is about ensuring your products help you reach your business goals. UX design, on the other hand, takes those business goals and turns them into user journeys. By clearing up common misconceptions and understanding the similarities and distinctions between product design Vs. UX design, you may be able to improve the quality of your business and its management and development.
Beyond simply making users happy, product design and user experience carry a lot of value. Having a strong market presence for your product can also help you protect it and give users the best experience possible. Effective design can lead to a higher ROI, lower development costs, more loyal customers, and conversion paths that work better.
FAQ
Who earns more UX designers or product designers?
Both UX designers and Product designers earn handsomely. According to the job portal, indeed, UX designers earn $99,000-100,000/ year. On the other hand, a product designer earns $110,000 – 124,000 (builtin)
Can you be a UX Designer without coding?
If you know to code, it’s indeed an added advantage. However, your design skills will always be the most desired skill. Also, knowledge about coding will surely help in designing better. Knowing how stylesheets work, knowing the tech stack being used, and knowing how browsers render designs are crucial because they are what are used to implement the designs and interactions you create.
What is an example of product design?
Coca-Cola, aka Coke bottle, is a prime example of product design. This iconic design was inspired by the cocoa plant, which has nothing to do with the drink. However, the bottle design is one of the most recognized designs in the world now.
Biggest weakness of a UX designer?
- Not able to collaborate
- Reluctant to learn new technologies
- Bad visual skills
- Being a perfectionist
- Not able to produce physical prototypes
Product design vs product management: How do they differ?
In the business world, the term “product management” refers to the function responsible for overseeing the whole development and release of a product. You, as a product manager, care deeply about the quality of both the product and the user experience, and you work to ensure that these priorities are in sync with the company’s larger strategic goals and objectives.
Product designers must be well-versed in PX (product experience) and UX (user experience), but they focus mainly on the UI and design to achieve CX (customer experience) objectives.