What is first click testing?
How much time would you spend on a trip if you took a wrong turn at the beginning of the journey? You might end up driving six hours instead of three to get to your destination.
When making the first turn, going in the wrong direction could have a devastating effect on completing the task. With digital goods, things aren’t vastly different.
Unlike web analytics tools that only tell you where the user clicked and not what they were trying to achieve, first-click testing allows you to understand the user behavior around each task separately.
First-click usability testing was introduced in 2006 by Bob Bailey and Cari Wolfson. According to their findings, if the first click is correct, the chance for users to complete the action correctly is 87%, as opposed to 46%, if the first click goes wrong.
How does first click testing work?
During first click testing, the user is provided with a task and an image of an interface and is asked where they would click first to complete the given task.
The position of the click, along with the duration they took to make the click is recorded. The reason why they clicked in where they did could be collected through further feedback.
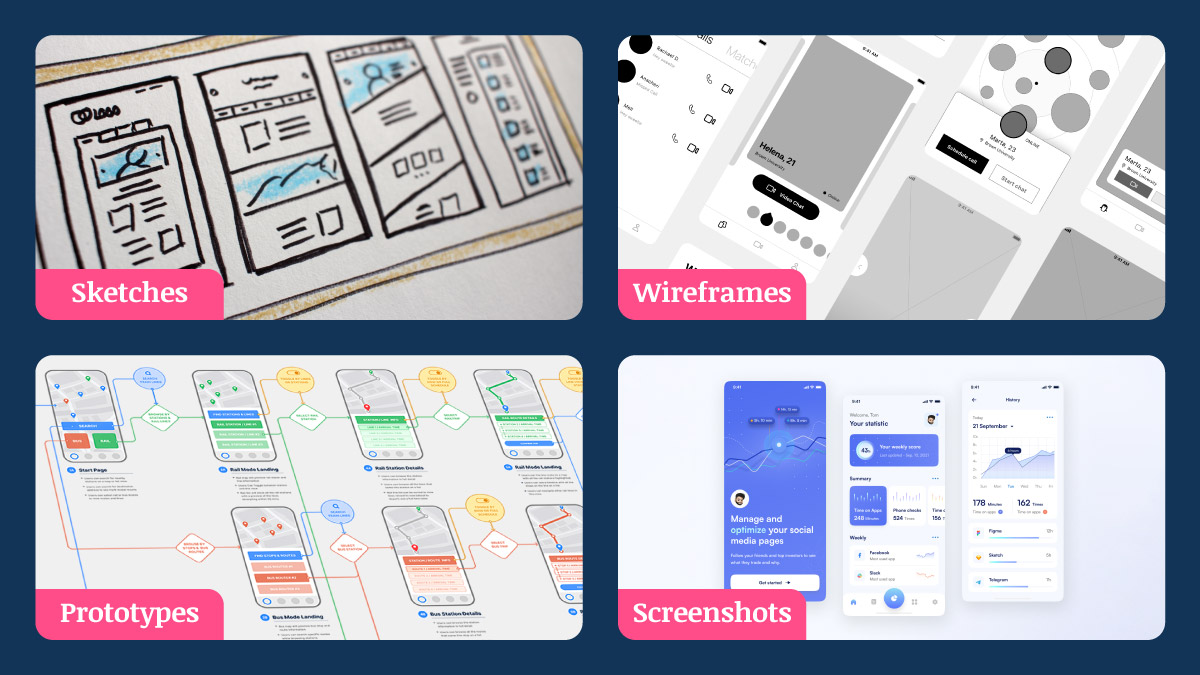
This test can be done using screenshots, wireframes, prototypes, and sketches- right from the early stages of the design process to the final designs and live interfaces.
Why should we do click testing in UX research?
To address the following issues, a first click test should be carried out.
- Do participants understand where to click to reach XXX?
- Where do users click for a certain task? Why?
- Does the arrangement or the hierarchy make sense?
- What is the overall experience of people with the product or design?
- How lost are people when they use the product?
Let’s see how the first click test helps an organization achieve its goals.
-
Customer Success
Giving customers the satisfaction they expect is the first step to a brand’s success. First click testing helps in optimizing the interface for a better user experience.
A user-friendly design is more likely to take the customers towards their final action than something that creates confusion among them.
-
Reusable testing
One of the greatest advantages of first click testing is that the same test can be reused throughout the development process. It provides the developers with a clear-cut idea of the success rate of the product.
-
Informed decision making
While a participant is asked to complete a given task, first click testing also records the time taken for the click. Alternative designs could then be made by comparing the time taken to complete different tasks.
The interface that yields the fastest completion rate can then be chosen.
When to conduct first-click tests in UX research?

First click testing is an inexpensive method that could be used to test which design will work best for your brand.
This testing method could be used on a wireframe, which means the app or website doesn’t even need to be existing at the time of testing. The users are asked to demonstrate where they are most likely to click if the buttons were active.
Taking the first click testing at each stage of development is not necessary. Testing conducted during the initial stages of development tends to be less expensive than testing conducted during the final stages of development.
Keeping an eye on the analytics will help in implementing the first click testing at the right time. If the analytics tool shows high bounce rates, low conversion rates, or more page time, it could suggest navigation problems, which could be fixed through first-click testing.
How to create successful first click tests?
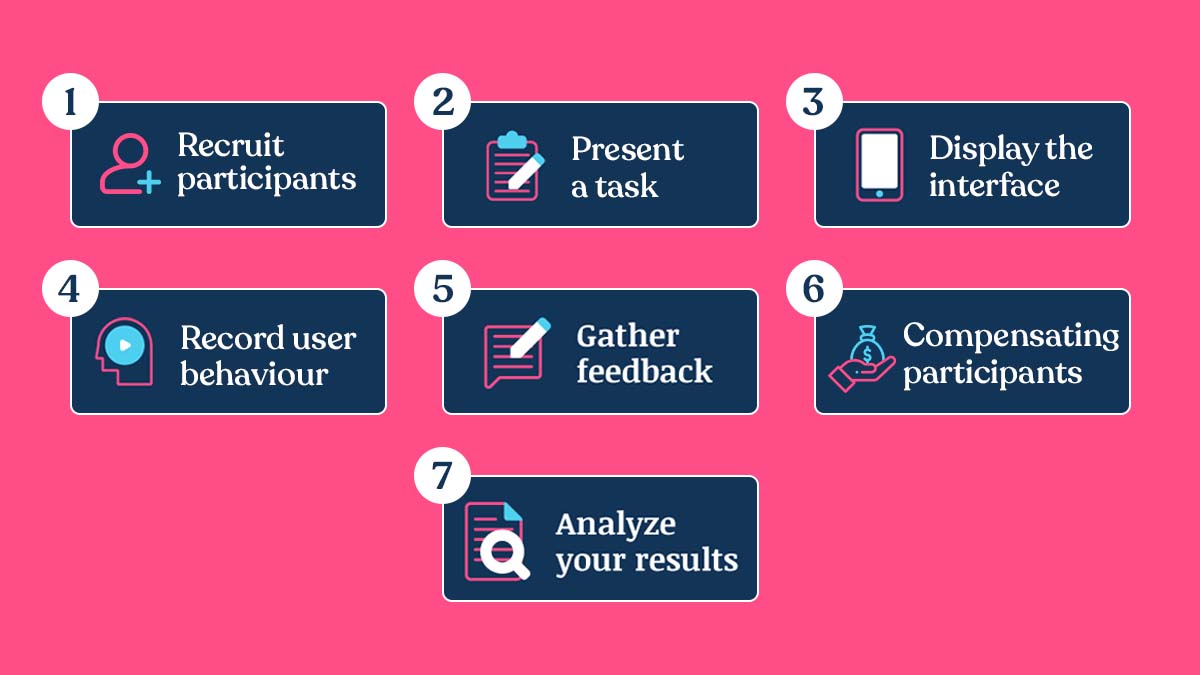
Following are the steps that could be followed to create a click test.
-
Recruit Participants
The first step towards effective first click testing or user research studies is recruiting participants that match your user personas. It is recommended to aim for 100–500 participants, as it will yield more reliable data than a click test with fewer people.
-
Present a task
Provide the user with a task. Ensure that they see the interface only after you provide them with the task so that the reaction time can be recorded. Choose the task by analyzing your customer journey map, which shows various roadblocks.
Present the customer with a broad, simple, and relative task. For example,
“Please click where you would click to add a product to the shopping cart.”
-
Display the interface
Once the task becomes clear to the customer, show them the website, app, or software. While conducting the first click test, the interface doesn’t need to be in the final stage. Depending on where you are in the development process, it could be a prototype, a product screenshot, or even a wireframe sketch.
-
Record user behavior
Once the interface is displayed, record the user’s actions. This helps analyze two metrics; where the user clicked and how long it took them to click.
These two metrics measure the difficulty level of the task. After testing different users, the usability of the product or feature can be determined from the data.
-
Gather feedback
After the testing, survey the users to find out why they behaved the way they did. If any users click on a least expected area, ask them the reason. If any users took longer to click, ask them whether they faced any confusion.
A system usability scale can be used to gather feedback in a perfect form.
-
Compensating Participants
In the context of research, compensation can be anything provided to testers in exchange for taking part in the study. It is critical to determine the methods and previously used usability test compensation factors when determining how and how much to compensate participants for their time.
-
Analyze your results
Begin with the percentage of users who were unable to complete the task. If the percentage seems so high, determine where they clicked and why they did so. Consider the demographics of these users, and come up with potential changes to satisfy this segment of your target audience.
For the users who completed the task, determine the time taken to make the click. The less time it takes, the more user-friendly your design is. One of the easiest ways to do this is to ask an employee to do the task. If both the employee and the user take almost the same amount of time, then the feature is easy to use.
Key benefits of first click testing
Knowing where people are likely to click greatly helps in product design. Clicks in the least expected areas highlight confusion among the users and can be kept in mind for future design processes.
First click testing gives an insight into users’ expectations, particularly for common interface elements such as menus and buttons.
Recording the time taken for users to make the click and comparison among them help in determining the usability of a particular product or feature.
How to track clicks?
First click testing can either be done in person or by using software, depending on the budget, the number of responses needed, and the amount of time you have.
Many tools can be used for tracking clicks. They could show you not only where the users click but also where they mouse around in search of the next thing to click. These testing tools could also tell you the most common pathway the users take to complete a given task.
You can also use testers who represent your target audience. Some services can provide paid testers from whatever demographics you require. Some of them are given below.
Questions to ask participants
After deciding on the primary research question, choose the questions you’ll use to guide the testers. One of the smartest ways to get accurate results is by encouraging the testers to behave like users by providing them with a task.
For example, replace “Where would you click to choose your shoe size?” with “Here is a page full of shoes of different sizes, how will you buy the one for you?”
Some of the tips to follow while preparing the questions are as follows:
- Avoid using questions that already have hints about the answers.
- Avoid using jargon and technical terms.
- Do not assign more than ten tasks, as it could tire the users.
- After the completion of the test, do not disclose the correct answer. Users shouldn’t feel like there is a right or wrong answer.
Some of the problems that could prevent the users from making the right click are:
- Counterintuitive menu labels
- Confusing navigation pathways
- Misleading labels
- Buttons are hard to find because of their color or size.
How to analyze your test results?
The first thing to assess while analyzing the test result is whether the users clicked on the expected place or not.
By observing the user pattern, one could redesign the interface so that the user journey will naturally flow from one thing to another. A cluster of wrong answers in the heat map could suggest confusion generated among the users while accomplishing the given task.
Clicks could be measured in percentage
if the number of clicks possible on a page is figured out. Using percentages instead of the count of clicks, different results could be easily compared.
Measuring the time taken to make the click is another important factor. Users taking a relatively long time indicates confusion.
Task completion doesn’t always mean an effective user interface. So, measuring the time taken to click is another important factor. Taking a long time to decide indicates confusion. On the other hand, if the users reach the wrong option quickly, that could suggest something that looks so much like the right option that they don’t see the right option.
Software used for first click testing

-
UsabilityHub
UsabilityHub is a tool that could tell us so much more than where the user clicked. It provides click cluster maps that display customer answers to follow-up questions when you hover over a cluster.
It also provides a funnel visualization tool that could help us understand where the users drop off most frequently on our live interface.
Price: Starts free, up to $398 per month.
-
UserZoom
UserZoom is a product testing tool that defines multiple parameters during testing. These parameters are combined into one single report that displays a range of metrics on your click test.
This allows you to measure one scenario for various metrics other than click placement and timing.
Price: Variable
-
Optimal Workshop
Optimal Workshop is a tool that is used to determine the first impression of a design. It provides feedback on interface layouts and makes it easy to create first-click testing.
While using this tool, you only need to create the task, and the tool will do the rest for you. This way, a lot of time could be saved.
Price: Starts free, up to $166 per month.
-
HubSpot
HubSpot offers unique content staging and preview tools that simulate a live version of your website or email. This tool allows you to run A/B testing on web pages and emails to determine which design performs better on the target audience.
Manual first click testing can be used through HubSpot’s click map tools.
Price: Starts free, up to $3, 200 per month
-
Hotjar
Hotjar is a powerful tool that reveals the user’s online behavior and voice. By combining analysis and feedback tools, Hotjar provides a clear picture of how to improve the user experience. The analysis tool includes heatmaps and session recordings.
Price: Hotjar includes a basic plan, which is free.
Final Note…
Users of digital products like websites, web applications, and mobile apps are often confused due to the complicated menu structures and a lack of apparent first click targets that hinder task completion.
First click testing plays an essential role in the UX research process. as it can help figure out how well the interface works and make changes or new ones based on what the user wants, not what the designer thinks they want.
Some other reliable methods for figuring out “How do people locate the right option?” or “Which is more easy-to-use?” are tree testing, preference tests, and the lostness measure.







